Controlling Diabetes can avoid Birth defects
Controlling Diabetes can avoid Birth defects
Brought to U....http://successgain.us and http://successgain.info
Brought to U....http://successgain.us and http://successgain.info
My memories
Controlling Diabetes can avoid Birth defects
Posted in 2015
Controlling Diabetes can avoid Birth defects
Posted in 2015
Controlling your blood sugar level before and during pregnancy is the best way to prevent diabetes complications. Good blood sugar control during pregnancy can:
Reduce the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Good blood sugar control reduces the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth — primary concerns for pregnancy and diabetes, as patients with uncontrolled diabetes have a higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth.
Reduce the risk of premature birth. The better your blood sugar control, the less likely you are to go into preterm labor.
Reduce the risk of birth defects. Good blood sugar control before and during early pregnancy greatly reduces your baby's risk of birth defects, particularly those affecting the brain, spine and heart.
Reduce the risk of excess fetal growth. If you have poor blood sugar control, extra glucose can cross the placenta, resulting in your baby growing too large (macrosomia). A large baby makes vaginal delivery difficult, increases the risk of a cesarean delivery and puts the baby at risk of injury during birth.
Prevent complications for mom. Good blood sugar control reduces your risk of urinary tract infections and yeast infections. It can also help avoid diabetic complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis. With diabetic ketoacidosis, your blood sugar is so high that your body fails to make enough insulin, resulting in a buildup of chemicals called ketones in your blood, and requiring hospitalization for management.
Prevent complications for baby. Sometimes babies of mothers who have diabetes develop low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) shortly after birth because their own insulin production is too high. Good blood sugar control can help promote a healthy blood sugar level for your baby, as well as healthy levels of calcium and magnesium in the blood.
Good blood sugar control also helps prevent a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes (jaundice) after birth, and decreases the risk of developing too much amniotic fluid around the baby — a condition known as polyhydramnios
Reduce the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Good blood sugar control reduces the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth — primary concerns for pregnancy and diabetes, as patients with uncontrolled diabetes have a higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth.
Reduce the risk of premature birth. The better your blood sugar control, the less likely you are to go into preterm labor.
Reduce the risk of birth defects. Good blood sugar control before and during early pregnancy greatly reduces your baby's risk of birth defects, particularly those affecting the brain, spine and heart.
Reduce the risk of excess fetal growth. If you have poor blood sugar control, extra glucose can cross the placenta, resulting in your baby growing too large (macrosomia). A large baby makes vaginal delivery difficult, increases the risk of a cesarean delivery and puts the baby at risk of injury during birth.
Prevent complications for mom. Good blood sugar control reduces your risk of urinary tract infections and yeast infections. It can also help avoid diabetic complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis. With diabetic ketoacidosis, your blood sugar is so high that your body fails to make enough insulin, resulting in a buildup of chemicals called ketones in your blood, and requiring hospitalization for management.
Prevent complications for baby. Sometimes babies of mothers who have diabetes develop low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) shortly after birth because their own insulin production is too high. Good blood sugar control can help promote a healthy blood sugar level for your baby, as well as healthy levels of calcium and magnesium in the blood.
Good blood sugar control also helps prevent a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes (jaundice) after birth, and decreases the risk of developing too much amniotic fluid around the baby — a condition known as polyhydramnios
My advise
1.. High blood sugar can cause problems all over the body. It can damage blood vessels and nerves. It can harm the eyes, kidneys, and heart. In early pregnancy, high blood sugar can lead to birth defects in a growing baby.
2...During pregnancy, an organ called the placenta gives a growing baby nutrients and oxygen. The placenta also makes hormones. In late pregnancy, the hormones estrogen, cortisol, and human placental lactogen can block insulin. When insulin is blocked, it’s called insulin resistance. Glucose can't go into the body’s cells. The glucose stays in the blood and makes the blood sugar levels go up.
3.. Birth complications if diabetes is uncontrolled
1.. High blood sugar can cause problems all over the body. It can damage blood vessels and nerves. It can harm the eyes, kidneys, and heart. In early pregnancy, high blood sugar can lead to birth defects in a growing baby.
2...During pregnancy, an organ called the placenta gives a growing baby nutrients and oxygen. The placenta also makes hormones. In late pregnancy, the hormones estrogen, cortisol, and human placental lactogen can block insulin. When insulin is blocked, it’s called insulin resistance. Glucose can't go into the body’s cells. The glucose stays in the blood and makes the blood sugar levels go up.
3.. Birth complications if diabetes is uncontrolled
- Stillbirth (fetal death). Stillbirth is more likely in pregnant women with diabetes. The baby may grow slowly in the uterus due to poor circulation or other conditions, such as high blood pressure or damaged small blood vessels. The exact reason stillbirths happen with diabetes is not known. The risk of stillbirth goes up in women with poor blood glucose control and with blood vessel changes.
- Birth defects. Birth defects are more likely in babies of diabetic mothers. Some birth defects are serious enough to cause stillbirth. Birth defects usually occur in the first trimester of pregnancy. Babies of diabetic mothers may have major birth defects in the heart and blood vessels, brain and spine, urinary system and kidneys, and digestive system.
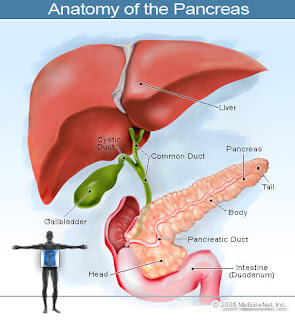
- Macrosomia. This is the term for a baby that is much larger than normal. All of the nutrients the baby gets come directly from the mother's blood. If the mother's blood has too much sugar, the pancreas of the baby makes more insulin to use this glucose. This causes fat to form and the baby grows very large.
- Birth injury. Birth injury may occur due to the baby's large size and difficulty being born.
- Hypoglycemia. The baby may have low levels of blood glucose right after delivery. This problem occurs if the mother's blood glucose levels have been high for a long time. This leads to a lot of insulin in the baby’s blood. After delivery, the baby continues to have a high insulin level, but no longer has the glucose from the mother. This causes the newborn's blood glucose level to get very low. The baby's blood glucose level is checked after birth. If the level is too low, the baby may need glucose in an IV.
- Trouble breathing (respiratory distress). Too much insulin or too much glucose in a baby's system may keep the lungs from growing fully. This can cause breathing problems in babies. This is more likely in babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia. Women with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes are at increased risk for preeclampsia during pregnancy. To lower the risk, they should take low-dose aspirin (60 to150 mg a day) from the end of the first trimester until the baby is born .
- Control your diabetes before and after conceiving can .avoid birth defects
Brought to U ..... http://successgain.info


Comments
Post a Comment