Importance of Minerals
Importance of Minerals

Brought to U...http://successgain.us and http://successgain.info
My memories
Importance of Minerals
Posted in 2011
A large number of minerals are present in the body. Some of these form part of body structural components and some others act as catalytic agents in many body reactions.
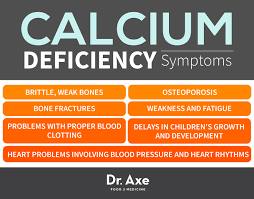
Calcium
Calcium is an element found in bones, shells and limestone, among other materials.
Calcium:
• helps lower blood pressure and control heartbeat
• helps regulate muscle contractions
• plays a role in blood clotting
• prevents fatal bleeding from breaks in the walls of blood vessels
• maintains cell membranes
• aids in the absorption of vitamin B12
• activates enzymes such as lipase, the fat-splitting enzyme
Your bones furnish reserves of calcium to keep plasma constant at all times.
Phosphorous
Phosphorus is a mineral. It is a major component of bones and teeth and makes up part of DNA and RNA.
Phosphorus serves as the main regulator of energy metabolism in cells, helps the body absorb glucose and transport fatty acids, and is part of the buffer system that helps control the acid-base balance of the body.
Iron
Iron is part of haemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying component of the blood. Iron-deficient people get tired easily because their bodies are starved for oxygen. Iron is also part of myoglobin, which helps muscle cells store oxygen. Without enough iron, ATP (the fuel the body runs on) cannot be properly synthesized. As a result, some iron-deficient people become fatigued even when their hemoglobin levels are normal. Although iron is part of the antioxidant enzyme catalase, iron is not generally considered an antioxidant, because too much iron can cause oxidative damage.
The most absorbable form of iron, called "haeme" iron, is found in oysters, meat, poultry, and fish. Non-haeme iron is also found in these foods, as well as in dried fruit, molasses, leafy green vegetables, wine, and most iron supplements. Acidic foods (such as tomato sauce) cooked in an iron pan can also be a source of dietary iron.
A common adult dose is 100 mg per day. It's not serious (such as normal menstrual blood loss or blood donation). Occasionally, however, iron deficiency signals ulcers or even colon cancer. Many premenopausal women become marginally iron deficient unless they supplement with iron. Even so, the 18 mg of iron present in most multiple-vitamin/mineral supplements is often adequate.
Sodium
Healthy American adults should eat no more than 2,300 milligrams of sodium a day. This is about 1 teaspoon of sodium chloride (salt).
How to reduce the sodium in diet?
• Choose fresh, frozen or canned food items without added salts.
• Select unsalted nuts or seeds, dried beans, peas and lentils.
• Limit the amount of salty snacks you eat, like chips and pretzels.
• Avoid adding salt and canned vegetables to homemade dishes.
• Select unsalted, fat-free broths, bouillons or soups.
• Select fat-free or low-fat milk, low-sodium, low-fat cheeses, as well as low-fat yogurt.
• Specify what you want and how you want it prepared when dining out. Ask for your dish to be prepared without salt.
• Use spices and herbs to enhance the taste of your food.
Potassium (K):
Potassium is a trace mineral essential for growth and good health.
Potassium in the human body helps to:
• keep normal water balance between the cells and body fluids
• maintain normal blood pressure
• transmit nerve impulses
• enable the contraction of muscles
• ensure proper functioning of cellular enzymes
Brought to U...http://successgain.us and http://successgain.info


Comments
Post a Comment